Linpack benchmark in DP (double precision, 64bit)
When the initial linpack was released in 1979 minicomputers like the PDP-11 (from 1970) had just moved from 16bit to 32bit with superminicomputers like the VAX-11 (1978). The supercomputer Cray-1 uses 64bit for data since 1975. By the time the TOP500 of fastest supercomputers was created in 1993 most supercomputers were using 64bit. For comparison this value is been used ever since.
64bit for normal citizens took a little longer. In 2003 AMD starts shipping the Athlon 64 processor lines with the first x86-based 64-bit processor architecture. For smartphones to move to 64bit it took until 2013 with the iPhone 5S.
- Phoronix Test Suite
- Fast test precompiled for Windows
- Install HPLinpack 2.3 on Ubuntu
- Paper from ICIST 2017 results
- HPL by Intel
Test with the Phoronix Test Suite

It can be installed in WSL or Ubuntu with:
sudo apt install php php-cli php-xml
git clone https://github.com/phoronix-test-suite/phoronix-test-suite/
cd phoronix-test-suite
sudo ./install-sh
phoronix-test-suite benchmark hpl

Some of my results are uploaded to openbenchmarking.org.
| Machine | CPU | MHz | FLOPS | Cores | architecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Uno R3 | ATmega328P | 16 | 94,300 | 1 | 8-bit AVR RISC - 350nm, 1997 |
| Jetson Nano A02 🟢 | Tegra X1 | 1500 | 3,848,500,000 | 4 | Cortex-A57 - 20nm, 2019 |
| Raspberry Pi 4 | BCM2711B0 | 1500 | 5,342,200,000 | 4 | Cortex-A72 - 40nm, 2019 |
| Elitebook hp8460p 🔵 | i5-2520M | 3200 | 37,275,300,000 | 2 | Sandy Bridge - 32nm, 2011 |
| hp zBook 15 G3 🔵 | i7-6820HQ | 3600 | 99,997,800,000 | 4 | Skylake - 14nm, 2015 |
| Xigmatek Gemini 🔵 | i3-10100 | 4038 | 132,278,500,000 | 4 | Comet Lake - 10nm, 2019 |
| hp mini 400 G9 🔵 | i7-13700T | 1840 | 235,712,000,000 | 16 | Raptor Lake - 7nm, 2022 |
| hp MT 600 G4 🔴 | RX 6600 | 2044 | 570,000,000,000 | 1792 | RDNA2 - TSMC N7, 2021 |

This number can be measured much faster with OpenCL. Some results for CPUs and GPUs are in the GPU benchmark section.
In this section I also included a graph for comparison of GFLOPS with DP (fp64) from the fastest supercomputer of their time to consumer hardware a few years later (source Google Sheet):
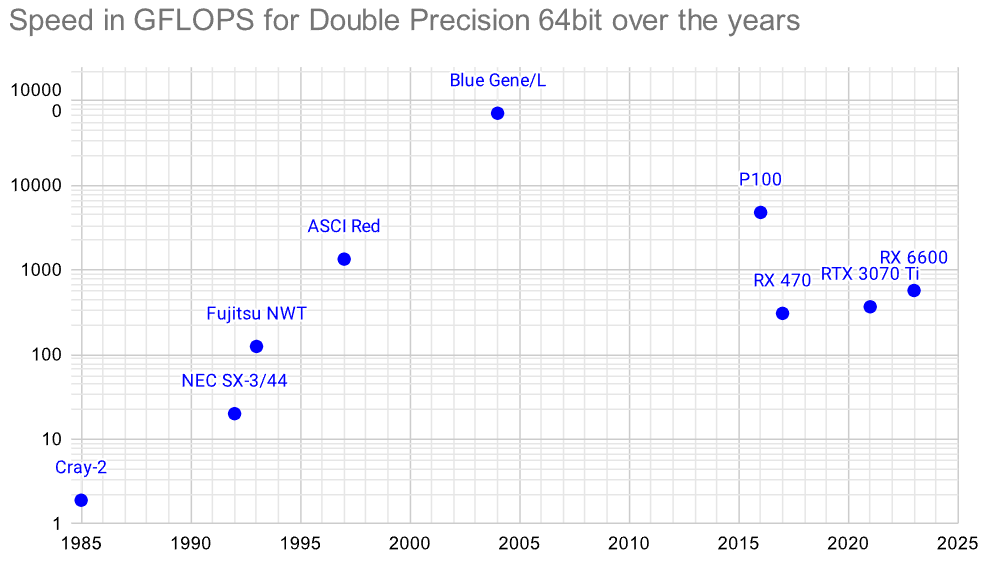
Earlier graph:
Speed comparison on Windows
With this download https://www.techpowerup.com/download/linpack-xtreme/ you don’t need to follow the longer steps on Ubunto below or install the phoronix test suite (might not work on smaller systems like Raspberry Pi 1). Results:
| CPU | MHz | FLOPS | source | architecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATmega328P | 16 | 94,300 | paper | 8-bit AVR RISC - 350nm, 1997 |
| RPi 3 | 1,200 | 3,381,000,000 | Roy Longbottom, update | Cortex-A53 |
| RPi 4 | 1,800 | 13,507,000,000 | Forum RaspberryPi, Roy Longbottom | Cortex-A72 |
| RPi 5 | 2,400 | 35,169,000,000 | Quad-core | Cortex-A76 |
| i7-6820HQ | 3,600 | 99,997,800,000 | - | Skylake - 14nm, 2015 |
| i3-10100 | 4,038 | 132,278,500,000 | - | Comet Lake - 10nm, 2019 |
Downloaded from https://www.techpowerup.com/download/linpack-xtreme/.
Install HPLinpack 2.3 on Ubuntu
1. Install dependencies
sudo apt-get install -y libatlas-base-dev mpich libmpich-dev gfortran
2. Download HPL
cd ~
wget https://www.netlib.org/benchmark/hpl/hpl-2.3.tar.gz
tar -xvzf hpl-2.3.tar.gz
mv hpl-2.3 hpl
3. Generate HPL template configuration file
cd hpl/setup
sh make_generic
cp Make.UNKNOWN ../Make.linux
cd ../
4. Modify Make.linux: Update paths for MPI and ATLAS libraries:
ARCH = linux
MPinc = /usr/include/mpich/
MPlib = /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libmpich.so
LAinc = /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/atlas
5. Compile HPL
make arch=linux -j $(nproc)
6. Modify HPL.dat and run HPL:
cd bin/linux
./xhpl
Full guide: Gist by Levi Hope
Paper from ICIST 2017 with results
| Platform | CPU/MCU | Architecture | MFlops | DMIPS | MHz | RAM kB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Uno R3 | ATmega328P | AVR 8bit RISC | 0.0943 | 10 | 16 | 2 |
| Embedded Pi | STM32F103RB | ARM Cortex-M3 (ARMv7-M) 32bit | 0.552 | 92 | 72 | 20 |
| Node MCU 1.0 | ESP8266 | Tensilica Xtensa LX106 32bit | 1.207 | 113 | 80 | 64 |
| Node MCU32 | ESP32s | Tensilica Xtensa LX106 32bit | 2.805 | 176 | 160 | 520 |
| NUCLEO F746ZG | STM32F746Z | ARM Cortex-M7 (ARMv7E-M) 32bit | 3.588 | 763 | 216 | 320 |
| Raspberry Pi 1B | BCM2835 | ARM1176 (v6) 32bit | 42.00 | 875 | 700 | 512000 |
| Raspberry Pi 2 | BCM2836 | ARM Cortex-A7 (v7-A) 32bit | 170.92 | 2019 | 900 | 1024000 |
| Raspberry Pi 3 | BCM2837 | ARM Cortex-A53 (v8-A) 32bit | 180.14 | 3039 | 1200 | 1024000 |
| LinpackDP | Dhrystone |
Read more in this article - paper ICIST 2017.
HPL by Intel
The multithread version to measure the performance of supercomputers there is the High Performance Linpack:
But you can’t just download it and make/compile the benchmark and run it. You need MPI, BLAS and VSIPL. A simple solution is to download the compiled binaries from Intel
For my i7-6820HQ it reached a maximum of 99.9978 GFlops for a size of 27000. That’s $10^{11}$.